Carbonyl
compounds are the compounds containing carbonyl group in their structure.
The compounds having carbonyl group in their structure are carboxylic acids,
esters, enones, aldehydes.
ENONES
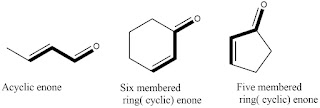
Enones
are basically the compounds having a ketone functionality and atleast one double bond in conjugation
with it in their structure. Enone acts as the chromophoric group of the compound
as it absorbs UV radiation. Some few basic examples of the enones is depicted
in diagram below.
Must read the general terms first from here for better understanding
Electronic transitions
Generally,
the carbonyl groups have the two possible transitions pi to pi*and n to pi* . The pi to pi* is allowed transition but the n to pi* transition is forbidden. If the carbonyl group is a part of conjugated
system of double bonds, the absorption becomes intense. The more the
conjugation is, the more intense pi to pi* transition becomes.
Out of both transitions, the pi to pi* transition varies in a predictable manner on the addition of different substituents to the compound. So, one can predict the wavelength at which the pi to pi* transition could occur. The rules for the calculation of wavelength are given by Woodward.
Empirical rules for Enones
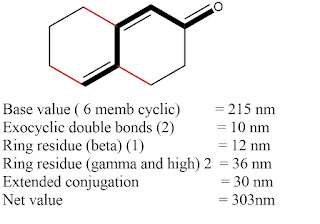
1. Base values for different enones
|
Parent
Compound |
Base
Value |
|
Acyclic
enone |
215
nm |
|
Acyclic
dienone |
245 nm |
|
Five
membered ring enone |
202
nm |
|
Six
membered ring enone |
215
nm |
2. Increment values.
|
To be applied for |
Increment value |
||
|
Alkyl or Ring residue |
alpha |
beta |
Gamma and higher |
|
10 |
12 |
18 |
|
|
Extended double bond
conjugation |
30 |
||
3. Polar group values.
|
Polar
group |
Value |
|||
|
alpha |
beta |
gamma |
Delta |
|
|
-OH |
35 |
30 |
50 |
- |
|
-OCH3 |
35 |
30 |
17 |
31 |
|
-OCOCH3 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
- |
|
-Cl |
15 |
12 |
- |
- |
|
-Br |
25 |
30 |
- |
- |
|
-NR2 |
- |
95 |
- |
- |
4. Exocyclic
double bond: 5 nm
5. Homocyclic
diene component: 39 nm
Some
solved examples are given below:
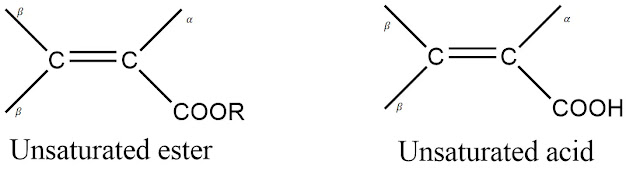
α,β- unsaturated Aldehydes
These aldehydes have almost same rules as that of enones except that their absorption values are shifted by about 5 to 6 nm towards shorter wavelength. Woodward’s rules for aldehydes are given below.
Base value
- for parent compound = 208 nm
- With α or β alkyl residue = 220 nm
- With α,β or β,β alkyl residue = 230 nm
- With α,β,β alkyl residue = 245 nm
α,β- Unsaturated Acids and esters
These carboxylic acids and esters also have same rules as that of enones. The values for carboxylic acids and esters given by Nielson are given below.
Base values
- With α or β alkyl residue = 208 nm
- With α,β or β,β alkyl residue = 217 nm
- With α,β,β alkyl residue = 225 nm





1 Comments
Valuable content 👌
ReplyDeleteLet me know your valuable suggestions and queries here.