Introduction
A radiation is basically the energy emitted in the
form of wave (light) or particle (photons). Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is
the energy which flows through the space or any medium in the form of EM waves.
EMR is formed due to the oscillating electric and magnetic fields at the right angle to each other.
 Image from weather.gov
Image from weather.govThe overall direction of movement of
the wave is perpendicular to the direction of oscillating electric and magnetic
fields. The radiation composes of energy packets called as photons.
General fundamentals
Amplitude is the distance from the medium of wave to the maximum vertical
displacement, in short- the height of the wave. The more is the amplitude, the
more will be energy of the wave or vice versa.

Wavelength refers to the distance associated with the one complete cycle
of oscillation. It can be from one crest to other crest or one trough to next
trough. The more the wavelength, the lesser will be the frequency and hence
energy. It is measured in metres, centimetres, micro meter.
Frequency refers to the number of complete oscillation cycles per second. Its
units are Hertz (Hz). The more is the frequency of the wave, the greater will
be the energy associated with it.
Wave number refers to the number of waves per centimetre (cm). It is
measured in cm-1 or kayser.
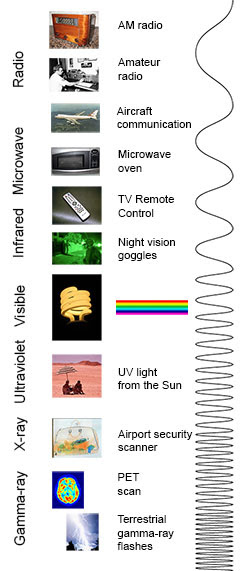
Types of Electromagnetic waves:
Based on the differing wavelengths and frequencies of the
waves, Electromagnetic spectrum composes of following different types of waves:
|
TYPE OF WAVE |
WAVELENGTH |
|
Cosmic rays |
10-9 nm |
|
Gamma rays |
0.2 –1 Angstrom (A) |
|
X- Rays |
1- 10 A |
|
Ultraviolet Radiation |
200 -400 nm |
|
Visible Radiation |
400- 800 nm |
|
Infrared Radiation |
2.5 – 25 µ |
|
Microwaves |
0.1 – 100 cm |
|
Radio Waves |
1 – 1000 m |
A general diagram showing the applications of different types
of EM Waves is given in Figure 1.3 below.
Types of transitions in various regions of EM spectrum are:
|
Electromagnetic
Region |
Type of
transition |
|
X- Ray |
Bond- breaking |
|
UV/Visible |
Electronic |
|
Infrared |
Vibrational |
|
Microwave |
Rotational |
|
Radiofrequency |
Nuclear spin (NMR), Electronic spin (ESR) |



0 Comments
Let me know your valuable suggestions and queries here.